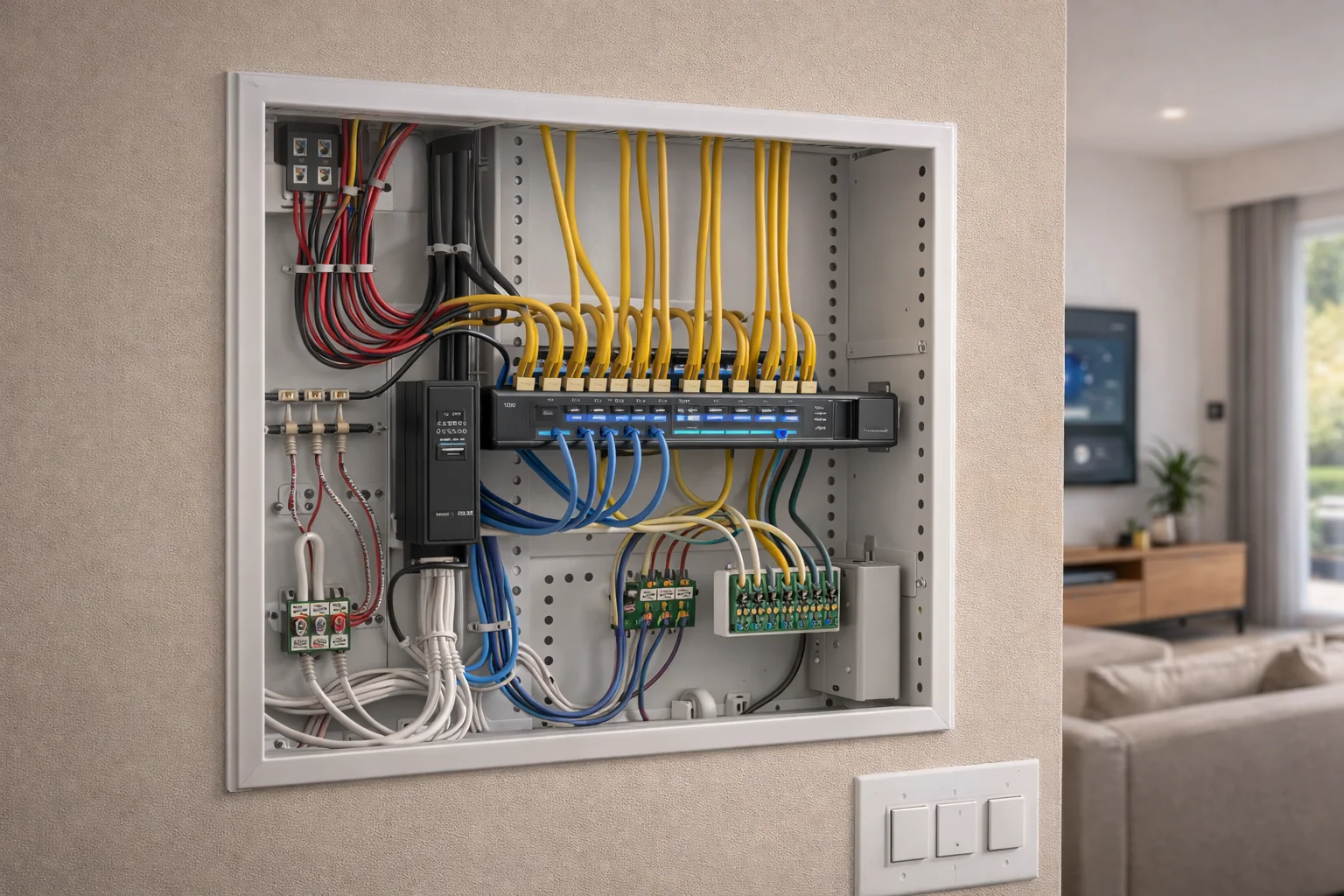
Low-voltage wiring is the backbone of a reliable smart home. It supports automation, security, audio, networking, and future technology—without relying solely on Wi‑Fi.
Introduction: The Part of Smart Homes Most People Overlook
When homeowners think about smart homes, they usually picture devices—screens, speakers, cameras, and apps. What they don’t think about is what connects everything behind the walls.
That hidden layer is low-voltage wiring, and it plays a bigger role in performance, reliability, and future-proofing than almost any device you can buy.
Understanding low-voltage wiring helps homeowners, builders, and remodelers avoid common mistakes and build smart homes that work well not just today—but for years to come.
What Is Low-Voltage Wiring?
Low-voltage wiring refers to cables that carry low electrical current, typically under 50 volts. These wires are used to transmit data, audio, video, and control signals, rather than power appliances.
In smart homes, low-voltage wiring supports systems such as:
Home automation
Internet and networking
Security systems
Cameras and access control
Audio and video distribution
Smart lighting controls
Motorized shades
Unlike standard electrical wiring, low-voltage systems focus on communication and coordination.
Common Types of Low-Voltage Wiring in Smart Homes
Ethernet (Cat5e / Cat6 / Cat6A)
Ethernet cabling forms the backbone of modern smart homes.
Used for:
Internet distribution
Smart home controllers
Security cameras
Wireless access points
Hardwired connections are faster, more secure, and more reliable than Wi‑Fi alone.
Speaker Wire
Speaker wiring enables:
Whole‑home audio
Home theater systems
Outdoor sound systems
Pre‑wiring speakers allows clean installations without visible wires later.
Coaxial Cable
While used less than in the past, coax still supports:
Cable and satellite TV
Antennas
Certain AV systems
It’s often included for flexibility and redundancy.
Control and Signal Wiring
These wires connect:
Keypads
Sensors
Motorized shades
Lighting control modules
They allow devices to communicate instantly and reliably.
Why Low-Voltage Wiring Matters for Smart Homes
1. Reliability
Wi‑Fi is convenient—but it’s not perfect.
Low‑voltage wiring provides:
Faster response times
Fewer dropouts
Consistent performance
This is critical for automation, security, and audio/video systems.
2. Scalability
Smart homes evolve.
Low‑voltage infrastructure makes it easy to:
Add devices later
Expand into new rooms
Upgrade systems without tearing into walls
Homes wired correctly from the start adapt easily to future technology.
3. Performance
Streaming, cameras, and automation all demand bandwidth.
Wired connections:
Reduce network congestion
Improve video quality
Support multiple systems simultaneously
This becomes more important as homes add more smart devices.
4. Clean, Professional Installations
Pre‑wiring keeps technology invisible.
Instead of:
Exposed cables
Power cords everywhere
Wi‑Fi extenders in every room
You get:
Centralized equipment
Clean wall plates
Organized systems
Low-Voltage Wiring vs Relying Only on Wi‑Fi
Wi‑Fi‑Only Homes
Easy upfront
Performance drops as devices increase
More troubleshooting
Low‑Voltage‑Ready Homes
Stable foundation
Better long‑term performance
Designed for growth
Most professionally designed smart homes use both, with wiring as the backbone and Wi‑Fi as the convenience layer.
When Should Low-Voltage Wiring Be Installed?
New Construction
This is the ideal time.
Walls are open
Costs are lower
Future upgrades are easy
Remodels
Strategic wiring can still be added during:
Major renovations
Room additions
Media room upgrades
Existing Homes
Even finished homes can benefit from targeted low‑voltage upgrades using creative routing and planning.
Low-Voltage Wiring for Builders and Homeowners
For Builders
Adds long‑term value
Differentiates homes
Reduces future change orders
For Homeowners
Better reliability
Cleaner installations
Fewer limitations later
Low‑voltage wiring is an investment in flexibility and performance.
Common Low-Voltage Wiring Mistakes
Skipping wiring to save short‑term costs
Running too few Ethernet lines
No central wiring location
Not planning for future needs
These mistakes are expensive—or impossible—to fix later.
How Professionals Plan Low-Voltage Wiring
Professional low‑voltage design starts with:
How you live in your home
Where technology will be used
What may be added later
The goal is not maximum wiring—it’s smart placement.
Final Thoughts
Low‑voltage wiring is the foundation that allows smart homes to work the way they’re supposed to.
When systems are built on solid infrastructure, technology becomes reliable, flexible, and easy to live with.
If you want a smart home that grows with you—not one you constantly fight—low‑voltage wiring is where it all begins.